PaddleOCR-VL-1.5: The 0.9B Parameter Revolution in Document Parsing
Core Question: How can a sub-1GB lightweight model achieve 94.5% accuracy in document parsing under real-world complex scenarios?
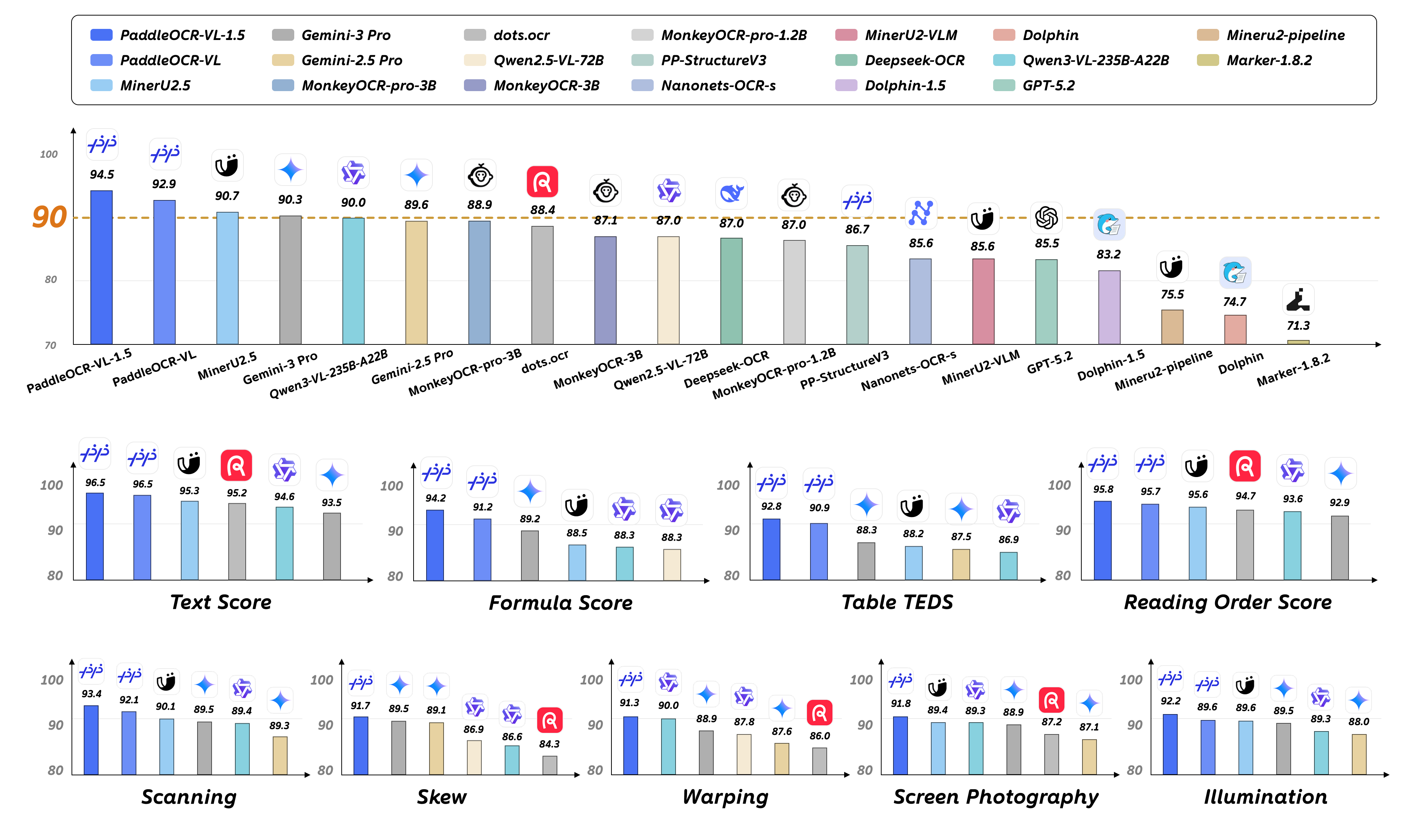
The answer is straightforward: PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 delivers. This vision-language model with only 0.9B parameters achieves 94.5% accuracy on OmniDocBench v1.5, surpassing all previous comparable models. More importantly, this isn’t laboratory performance under ideal conditions—it’s real-world capability across scanning artifacts, skew, warping, screen photography, and illumination variations.
My biggest takeaway from testing this model: finally, a model that understands real-world chaos. How many documents we process daily are perfectly scanned and perfectly aligned? Most are phone-captured receipts, tilted contracts, glare-affected screenshots. PaddleOCR-VL-1.5’s design philosophy starts from these real needs.
Why This Model Matters
Section Core Question: Among numerous document parsing tools, what pain points does PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 solve?
Traditional OCR tools perform adequately on well-formatted documents but fail dramatically when facing complex scenarios. Consider these situations:
-
You photographed a tilted contract with your phone and need to extract key clauses -
Scanned documents have obvious distortion and shadows -
You need to recognize table data from screen-captured photos -
Rare characters and special symbols in ancient texts -
Cross-page tables fragmented and difficult to integrate
These are problems I’ve repeatedly encountered in real work. Each time requires manual adjustment, re-photographing, or even manual input. PaddleOCR-VL-1.5’s emergence shows me a systematic solution.
Five Core Capability Breakthroughs
1. Balance Between Ultra-Lightweight and Ultra-Accurate
What does 0.9B parameters mean? This is a model size that can run on ordinary GPUs or even some high-end mobile devices. Yet it achieves 94.5% accuracy on OmniDocBench v1.5, with significant improvements in table, formula, and text recognition. This parameter efficiency stems from careful model architecture design and optimized training strategies.
My reflection: Small models don’t mean performance compromise. With deep focus in specific domains, small models can outperform generalized large models. This gives us insight—rather than pursuing universal large models, excel in vertical scenarios.
2. Irregular Shape Localization Capability
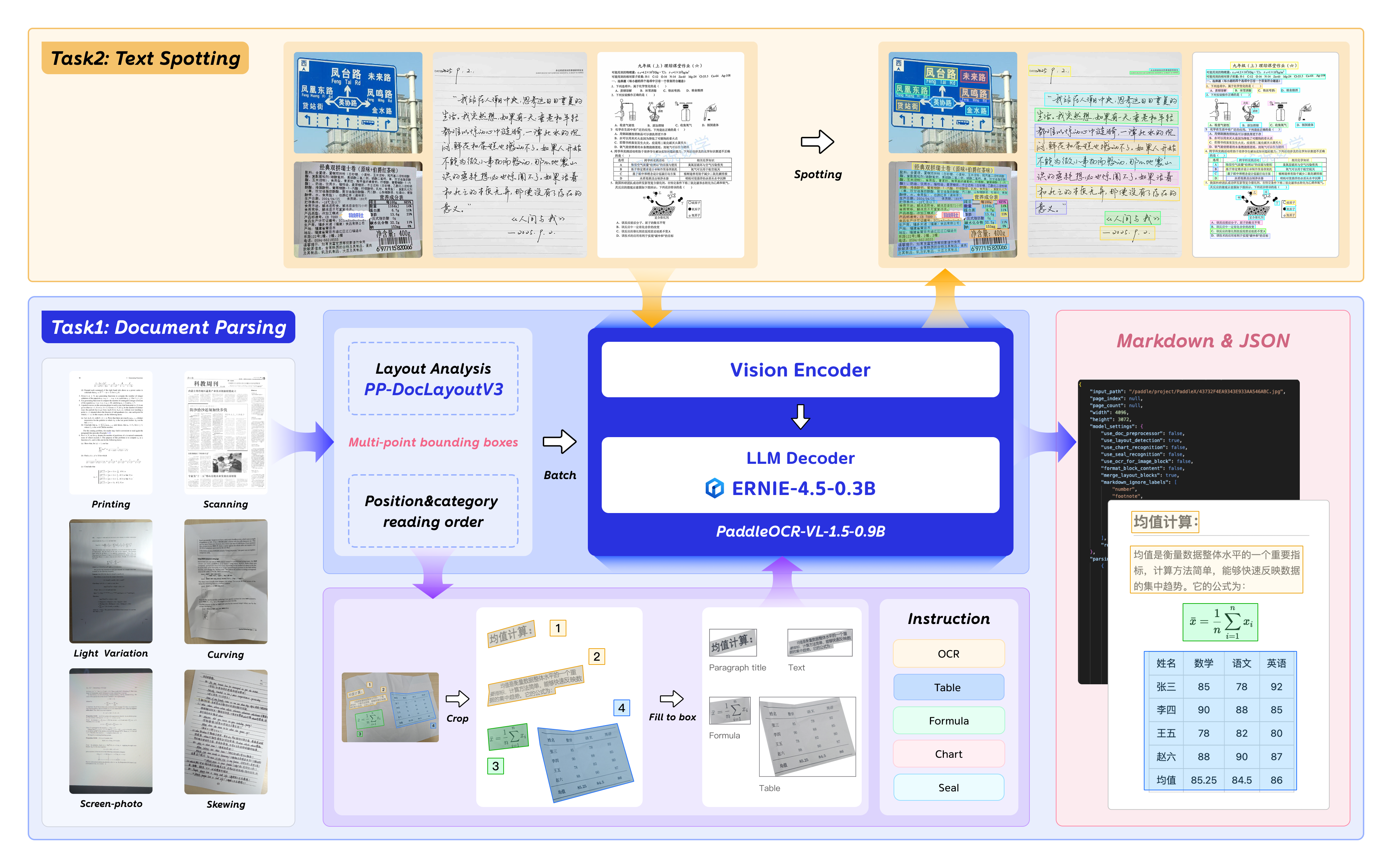
Traditional OCR typically only performs rectangular box detection, but real documents are often skewed and curved. PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 introduces polygonal detection capability, accurately handling localization under distorted document conditions. This is especially critical when processing scanned documents and curved book pages.
Real application scenario: Suppose you need to digitize an old ledger with yellowed, curled pages. Traditional tools might only recognize partial content or require you to laboriously flatten the pages. PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 can directly process curved pages, accurately extracting each text line through polygonal localization.
3. Integrated Text Spotting
The model adds text spotting functionality, not only recognizing text content but accurately annotating each text region’s position. This is crucial for scenarios requiring document layout preservation—such as legal document analysis and layout restoration.
4. Specialized Seal Recognition
In Chinese document processing, seal recognition is a special but important requirement. Seals in contracts, certificates, and official documents are not just content but markers of document validity. PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 specifically optimized seal recognition capability, setting new records on relevant metrics.
Scenario example: Enterprises need to batch process historical contracts and extract key information to build databases. Seal recognition and localization can quickly confirm document legal effectiveness and flag abnormal situations requiring manual review.
5. Multilingual and Special Scenario Enhancement
The model improves recognition of rare characters, ancient texts, multilingual tables, underlines, and checkboxes. Language coverage extends to Tibetan and Bengali. This diversity support enables the model to handle broader practical scenarios.
Lesson learned: Special scenario processing capability is the true touchstone of model practicality. Those seemingly marginal requirements are often users’ pain points.
Innovation in Long Document Processing
Automatic cross-page table merging and cross-page paragraph heading recognition—these two features solve the core difficulty in long document parsing: content fragmentation.
Imagine processing a 100-page research report with multiple cross-page tables and continuous chapters. Traditional tools would split cross-page tables into independent parts, and paragraph headings might be misidentified as regular text. PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 can understand document logical structure, automatically identifying and merging this content, significantly reducing post-processing manual work.
Understanding the Model Architecture
Section Core Question: How does PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 achieve such powerful capabilities at 0.9B parameter scale?
The model adopts a vision-language multimodal architecture, a design approach that fuses visual understanding and language processing capabilities. Simply put, the model doesn’t just “see” images but “understands” the semantics and structural relationships of text in images.
Unified Multi-Task Framework
PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 handles multiple tasks in a single model:
-
Text recognition (OCR) -
Table recognition -
Formula recognition -
Chart recognition -
Text spotting -
Seal recognition
The benefit of this unified framework is obvious: users don’t need to call different models for different tasks—one model handles all document parsing needs. From an engineering practice perspective, this significantly reduces deployment and maintenance costs.
Unique insight: The essence of multi-task learning is knowledge sharing. Inherent connections exist between different tasks—recognizing tables requires understanding text, recognizing formulas requires understanding symbols—these capabilities can mutually reinforce. The unified framework allows the model to leverage synergistic effects between different tasks during training.
Real-World Scenario Performance Validation
Section Core Question: How does PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 perform in actual complex environments?
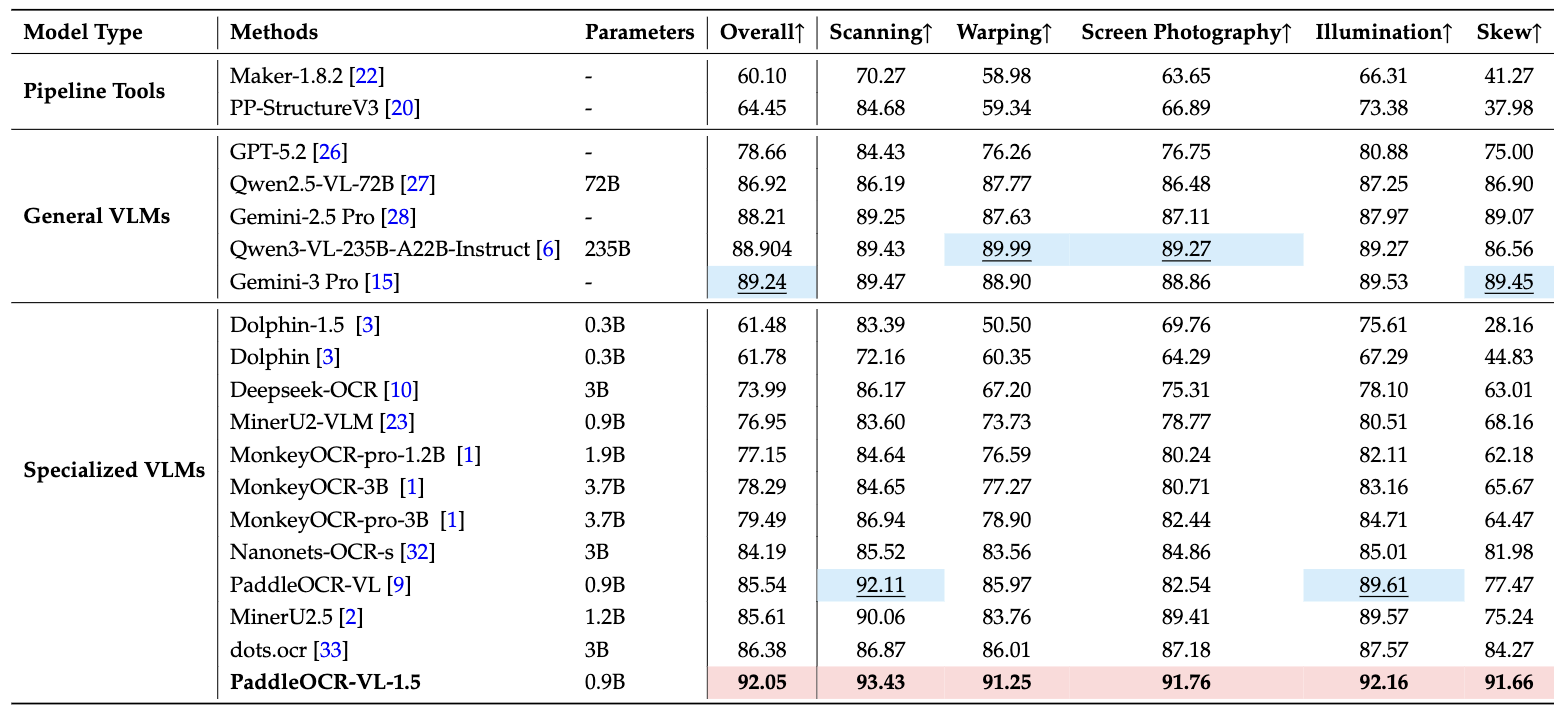
To rigorously evaluate model robustness against real-world physical distortions, the team constructed the Real5-OmniDocBench benchmark, covering five typical scenarios:
Scenario 1: Scanned Documents
Noise, shadows, and color distortion from the scanning process. Test results show PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 maintains high accuracy in scanning scenarios, significantly outperforming mainstream open-source and proprietary models.
Scenario 2: Skewed Documents
Angular deviation during document photography or scanning. This is one of the most common scenarios—when we photograph documents with phones, it’s difficult to ensure perfect perpendicularity. The model handles various skew angles accurately through irregular shape localization capability.
Scenario 3: Warped Documents
Physical deformation like curved book pages and folded documents. This is especially common when processing books and bound materials. The model’s polygonal detection capability plays a key role in this scenario.
Scenario 4: Screen Photography
Moiré patterns, reflections, and resolution loss from photographing computer or phone screens. This scenario frequently appears in remote work and online meetings—you need to save a document displayed on screen but don’t have the original file.
Scenario 5: Illumination Variation
Uneven lighting, shadows, overexposure, or underexposure. This situation is most easily encountered when photographing documents outdoors. The model needs to maintain stable recognition capability under various lighting conditions.
Performance Comparison Data
Across all five scenarios, PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 sets new performance records. This isn’t laboratory data but validation from real use scenarios.
My reflection: Benchmarks should align with actual use scenarios. Many models perform excellently on standard datasets but are helpless when facing real-world chaos. The construction of Real5-OmniDocBench itself is an important push for industry evaluation standards.
Quick Start Guide
Section Core Question: How to start using PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 in 5 minutes?
Environment Setup
First, install dependencies. Note the version requirements:
# Install PaddlePaddle for CUDA 12.6
python -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu==3.2.1 -i https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/packages/stable/cu126/
# Install PaddleOCR with document parser module
python -m pip install -U "paddleocr[doc-parser]"
Important note: Must install PaddlePaddle 3.2.1 or higher. macOS users need to use Docker environment. This is because the model uses specific framework features that may not work properly with older versions.
Command Line Quick Experience
The simplest usage is via command line:
paddleocr doc_parser -i https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/paddleocr_vl_demo.png
This command automatically downloads the model (first use), processes the specified image, and outputs recognition results. You can replace the URL with a local file path.
Python API Usage
A more flexible approach is using the Python API:
from paddleocr import PaddleOCRVL
# Initialize model
pipeline = PaddleOCRVL()
# Process image
output = pipeline.predict("https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/paddleocr_vl_demo.png")
# Handle results
for res in output:
res.print() # Print to console
res.save_to_json(save_path="output") # Save as JSON
res.save_to_markdown(save_path="output") # Save as Markdown
This code demonstrates the complete processing workflow: initialize model, process image, save results. Results can be saved as JSON or Markdown format for subsequent processing or direct reading.
Real application scenario: Suppose you need to batch process invoice images and extract key information like amounts and dates. You can pass a list of image paths to the model, process each image in a loop, save results as structured JSON, then import to database or Excel.
Performance Optimization: Using vLLM Acceleration
For large-scale batch processing, use vLLM inference server to boost performance:
Method 1: Start Service Using Docker
docker run \
--rm \
--gpus all \
--network host \
ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-genai-vllm-server:latest-nvidia-gpu \
paddleocr genai_server --model_name PaddleOCR-VL-1.5-0.9B --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8080 --backend vllm
Method 2: Use vLLM Directly
Refer to the PaddleOCR-VL usage guide in vLLM official documentation.
After starting the service, modify just one line in the calling method:
from paddleocr import PaddleOCRVL
# Use vLLM server
pipeline = PaddleOCRVL(
vl_rec_backend="vllm-server",
vl_rec_server_url="http://127.0.0.1:8080/v1"
)
output = pipeline.predict("your_image_path.png")
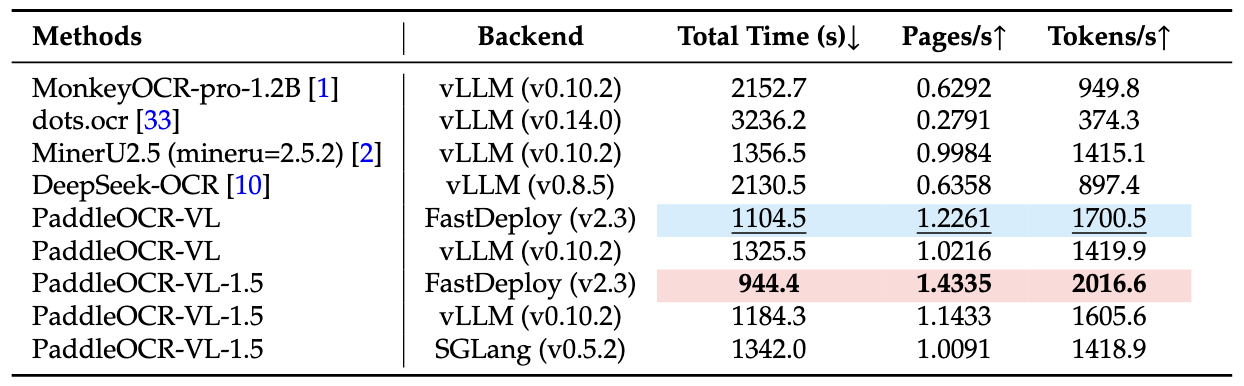
How much performance improvement? According to official tests, using vLLM on A100 GPU to process 512 batches of PDF documents from OmniDocBench v1.5, end-to-end inference time significantly decreases. This is especially important for enterprise scenarios requiring massive document processing.
Inference with Transformers Library
Section Core Question: How to integrate PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 in the Transformers ecosystem?
For developers familiar with the Hugging Face ecosystem, you can directly use the Transformers library to call the model. Note that the official recommendation is to use PaddleOCR’s standard method because it’s faster and supports page-level document parsing. The Transformers approach currently only supports element-level recognition and text spotting.
Install Dependencies
python -m pip install "transformers>=5.0.0"
Basic Inference Code
from PIL import Image
import torch
from transformers import AutoProcessor, AutoModelForImageTextToText
# Configuration parameters
model_path = "PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR-VL-1.5"
image_path = "test.png"
task = "ocr" # Options: 'ocr' | 'table' | 'chart' | 'formula' | 'spotting' | 'seal'
# Image preprocessing (spotting task needs special handling)
image = Image.open(image_path).convert("RGB")
orig_w, orig_h = image.size
spotting_upscale_threshold = 1500
if task == "spotting" and orig_w < spotting_upscale_threshold and orig_h < spotting_upscale_threshold:
process_w, process_h = orig_w * 2, orig_h * 2
try:
resample_filter = Image.Resampling.LANCZOS
except AttributeError:
resample_filter = Image.LANCZOS
image = image.resize((process_w, process_h), resample_filter)
# Set max pixels
max_pixels = 2048 * 28 * 28 if task == "spotting" else 1280 * 28 * 28
# Load model
DEVICE = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
model = AutoModelForImageTextToText.from_pretrained(
model_path,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16
).to(DEVICE).eval()
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_path)
# Build prompts
PROMPTS = {
"ocr": "OCR:",
"table": "Table Recognition:",
"formula": "Formula Recognition:",
"chart": "Chart Recognition:",
"spotting": "Spotting:",
"seal": "Seal Recognition:",
}
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "image", "image": image},
{"type": "text", "text": PROMPTS[task]},
]
}
]
# Inference
inputs = processor.apply_chat_template(
messages,
add_generation_prompt=True,
tokenize=True,
return_dict=True,
return_tensors="pt",
images_kwargs={
"size": {
"shortest_edge": processor.image_processor.min_pixels,
"longest_edge": max_pixels
}
},
).to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=512)
result = processor.decode(outputs[0][inputs["input_ids"].shape[-1]:-1])
print(result)
Performance Optimization: Using Flash Attention
For scenarios requiring further speed improvement and memory reduction, enable Flash Attention 2:
pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation
Modify model loading code:
model = AutoModelForImageTextToText.from_pretrained(
model_path,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2"
).to(DEVICE).eval()
Unique insight: Choosing inference methods requires balancing flexibility and performance. The Transformers approach provides more customization space, suitable for research and experimentation; the standard approach is optimized for production environments, suitable for actual deployment.
Deep Dive into Specialized Capabilities
Section Core Question: How does PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 perform on specific tasks?
Text Spotting Capability
Text spotting not only recognizes text content but precisely annotates positions. This is crucial in scenarios preserving document layout and layout analysis.
Application scenario examples:
-
E-book Layout Analysis: Extract original book layout information for reformatting or format conversion -
Form Understanding: Recognize positional relationships of fields in forms for automatic filling or data extraction -
Advertisement Monitoring: Detect text regions in images, analyze advertising content distribution
Seal Recognition Specialty
In Chinese document processing, seals are a special but critical element. PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 sets new records in seal recognition.
Practical application value:
-
Contract Review Automation: Automatically identify and verify seals when batch processing contracts -
Document Authenticity Detection: Use seal recognition to assist in judging document validity -
Archive Digitization: Seal recognition and recording in historical archives
Lesson learned: Vertical domain detail optimization can create irreplaceable value. Seal recognition seems niche but is a rigid demand in legal, financial, and government sectors.
Table Recognition Precision
Tables are among the most complex structures in documents. PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 shows significant improvement in table recognition accuracy, especially for multilingual tables and complex nested tables.
Performance data: On OmniDocBench v1.5 table recognition tasks, the model achieves SOTA level.
Scenario applications:
-
Financial Statement Digitization: Automatically extract numerical data from financial statements -
Scientific Literature Processing: Extract experimental data tables from papers -
Multilingual Report Processing: Process complex tables containing mixed Chinese-English content
Formula Recognition Capability
Mathematical formula and scientific symbol recognition is another technical challenge. The model’s improved accuracy in formula recognition enables application in academic literature processing.
Application directions:
-
Textbook Digitization: Convert paper textbooks to editable digital versions -
Paper Retrieval: Extract formulas from PDF papers, build searchable formula libraries -
Online Education: Automatically recognize student-uploaded handwritten formula assignments
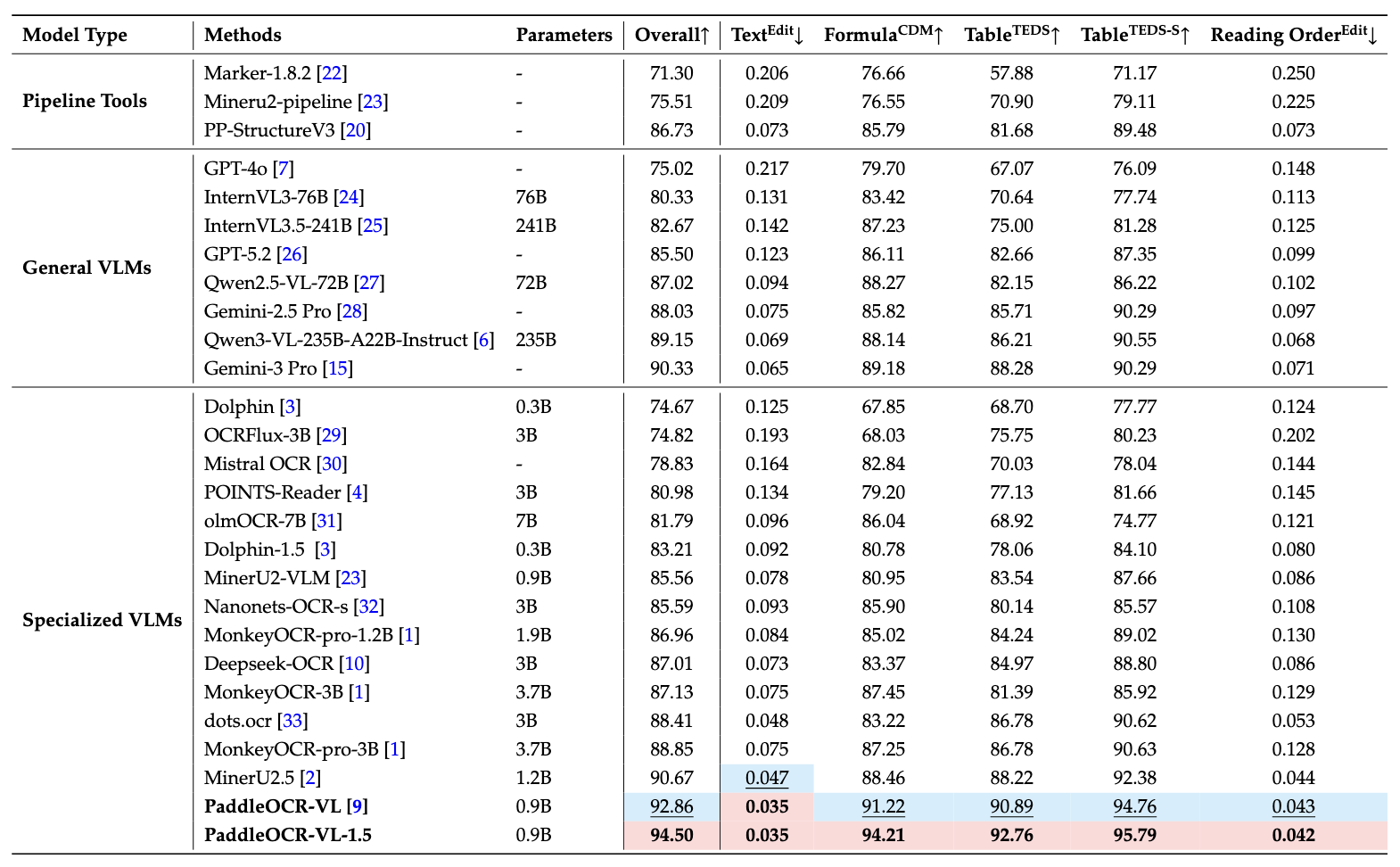
Comprehensive Performance Metrics Analysis
Section Core Question: Where are PaddleOCR-VL-1.5’s advantages compared to other models?
OmniDocBench v1.5 Benchmark Testing
On OmniDocBench v1.5, PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 achieves SOTA level in core metrics including overall accuracy, text recognition, formula recognition, table recognition, and reading order.
Note that except for Gemini-3 Pro, Qwen3-VL-235B-A22B-Instruct, and PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 which were independently evaluated, other models’ performance data are cited from the OmniDocBench official leaderboard.
Real5-OmniDocBench Real-World Scenario Testing
This is a brand-new benchmark specifically constructed for real-world physical distortion scenarios. The dataset is based on OmniDocBench v1.5 but adds samples from five typical scenarios: scanning, warping, screen photography, illumination, and skew.
Test results show PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 maintains the highest accuracy across all five scenarios. This proves the model performs excellently not only under ideal conditions but reliably in complex real environments.
My reflection: Real-world robustness is key to model practicality. Many research models perform amazingly in laboratories but encounter frequent problems once deployed to production environments. PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 considered real-world scenario complexity from the design inception.
Inference Performance
Processing 512 batches of PDF documents from OmniDocBench v1.5 on A100 GPU, PaddleOCR-VL-1.5’s end-to-end inference time includes the complete workflow of PDF rendering and Markdown generation. All methods use their respective built-in PDF parsing modules and default DPI settings, reflecting out-of-the-box performance.
Performance advantages manifest not only in accuracy but also in processing speed. This is crucial for enterprise scenarios requiring massive document processing—time is cost.
Practical Deployment Recommendations
Section Core Question: How to efficiently deploy PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 in production environments?
Hardware Selection
Choose appropriate hardware based on different scale requirements:
Small-Scale Deployment (daily processing <1,000 pages)
-
CPU: 8+ cores -
Memory: 16GB+ -
GPU: Optional (GTX 1660 or above)
Medium-Scale Deployment (daily processing 1,000-10,000 pages)
-
CPU: 16+ cores -
Memory: 32GB+ -
GPU: RTX 3090 or A4000
Large-Scale Deployment (daily processing >10,000 pages)
-
CPU: 32+ cores -
Memory: 64GB+ -
GPU: A100 or multi-GPU deployment -
Recommend using vLLM server
Performance Tuning Points
-
Batch Processing Optimization: For batch documents, properly setting batch size can significantly improve throughput -
Image Preprocessing: For high-resolution images, appropriate downsampling can accelerate processing speed -
Task Parallelization: Use multi-process or multi-threading to handle independent document tasks -
Result Caching: Implement result caching mechanism for repeatedly processed documents
Quality Assurance Strategies
-
Confidence Threshold: Set confidence threshold for recognition results; results below threshold are marked for manual review -
Key Field Validation: Add format validation and reasonability checks for critical business fields -
Sample Review: Regularly sample partial results for manual review to evaluate model performance -
Anomaly Monitoring: Monitor processing failure rate, average time consumption, and other metrics to detect anomalies promptly
Unique insight: Production deployment isn’t one-time work but a continuous optimization process. Establish comprehensive monitoring and feedback mechanisms, continuously adjusting configurations and strategies based on actual usage.
Insights from Technical Evolution
Section Core Question: What does the evolution from PaddleOCR-VL to PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 reveal?
PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 is the next-generation version of PaddleOCR-VL. From version evolution, I see several important trends:
From General to Scenario-Specific
Early models pursued generality—successfully handling various documents was considered success. But in practical applications, general often means mediocre. PaddleOCR-VL-1.5’s design philosophy is deep optimization for real scenarios while maintaining broad applicability.
The construction of Real5-OmniDocBench itself illustrates this point—we need tools that can handle real-world chaos, not models that score well on standard datasets.
From Large and Comprehensive to Small and Focused
In the era of large model prevalence, PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 insists on 0.9B parameter scale—this is courage. It proves that in vertical domains, carefully designed small models can outperform generalized large models.
This gives us an important insight: Not all problems need hundred-billion-level parameters to solve. Identify the problem domain, optimize deeply, and small models can create great value.
From Point Breakthroughs to Systematic Capabilities
PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 doesn’t just improve on certain metrics but builds a complete document understanding capability system: text recognition, table understanding, formula processing, localization capability, seal recognition, multilingual support, long document processing.
This systematic thinking is key to model practicality. Single capability breakthroughs often cannot solve practical problems; only forming complete capability loops can truly land applications.
Practical Workflow Recommendations
Section Core Question: How to efficiently use PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 in actual projects?
Document Batch Processing Workflow
import os
from paddleocr import PaddleOCRVL
from pathlib import Path
def batch_process_documents(input_dir, output_dir, task_type="ocr"):
"""
Sample workflow for batch document processing
Args:
input_dir: Input document directory
output_dir: Output result directory
task_type: Task type (ocr/table/formula, etc.)
"""
# Initialize model
pipeline = PaddleOCRVL()
# Ensure output directory exists
Path(output_dir).mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
# Supported file formats
supported_formats = ['.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.pdf']
# Traverse input directory
for filename in os.listdir(input_dir):
file_path = os.path.join(input_dir, filename)
# Check file format
if not any(filename.lower().endswith(fmt) for fmt in supported_formats):
continue
try:
# Process document
print(f"Processing: {filename}")
output = pipeline.predict(file_path)
# Save results
for res in output:
base_name = os.path.splitext(filename)[0]
res.save_to_json(save_path=os.path.join(output_dir, f"{base_name}.json"))
res.save_to_markdown(save_path=os.path.join(output_dir, f"{base_name}.md"))
print(f"Completed: {filename}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing {filename}: {str(e)}")
continue
# Usage example
batch_process_documents("./input_docs", "./output_results")
Result Validation and Post-Processing
Recognition results often require further validation and processing:
import json
def validate_and_clean_results(json_path):
"""
Example for validating and cleaning recognition results
"""
with open(json_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
data = json.load(f)
# Example: Extract text content and validate
text_content = data.get('text', '')
# Remove excess whitespace
text_content = ' '.join(text_content.split())
# Specific format validation (based on actual needs)
# For example: validate date format, amount format, etc.
return text_content
# Usage example
cleaned_text = validate_and_clean_results("./output_results/document.json")
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: What image formats does the model support?
Supports common image formats including PNG, JPG, JPEG, and PDF documents. For PDFs, automatic rendering processing is performed.
Question 2: How fast is processing? How long does a single image take?
Processing speed depends on hardware configuration and image complexity. On A100 GPU, single ordinary document image processing time is typically 1-3 seconds. Using vLLM server can significantly improve batch processing speed.
Question 3: How to handle multi-page PDF documents?
Directly pass in PDF file path; the model automatically processes multi-page content and supports cross-page table merging and paragraph recognition.
Question 4: How to optimize when recognition accuracy is unsatisfactory?
First check image quality, ensure sufficient clarity. For tilted or curved images, the model already has optimization, but in extreme cases, try preprocessing. For domain-specific terminology, consider using custom dictionaries (if supported in future versions).
Question 5: Can it run on CPU? How’s the performance?
Can run on CPU but speed will be significantly slower than GPU. For small-scale, non-real-time processing scenarios, CPU is a viable option.
Question 6: What languages does the model support?
Supports Chinese, English, as well as Tibetan, Bengali, and other languages. Also has good processing capability for multilingual mixed documents.
Question 7: How to integrate into existing systems?
Provides command-line tools, Python API, and Transformers interface in multiple ways. Choose the most suitable integration method based on existing system tech stack. vLLM server approach suits microservice architecture.
Question 8: What are model size and hardware requirements?
Model parameter scale is 0.9B, relatively lightweight. Recommend at least 16GB memory, GPU memory 8GB+. Can run on ordinary workstations or cloud servers.
Practical Operation Checklist
To help quick start, here’s a complete operation checklist:
Environment Configuration Checklist
-
[ ] Install PaddlePaddle 3.2.1 or higher -
[ ] Install PaddleOCR document parsing module -
[ ] (Optional) Install vLLM for inference acceleration -
[ ] (Optional) Install Flash Attention for optimization -
[ ] Verify GPU driver and CUDA version compatibility
Basic Function Testing Checklist
-
[ ] Run command-line example to verify installation -
[ ] Test Python API basic calling -
[ ] Test different task types (OCR, table, formula, etc.) -
[ ] Test batch processing function -
[ ] Test result saving and export
Production Deployment Checklist
-
[ ] Evaluate processing scale and hardware requirements -
[ ] Choose appropriate deployment method (standard/vLLM) -
[ ] Configure performance monitoring -
[ ] Establish quality validation process -
[ ] Develop exception handling strategy -
[ ] Prepare degradation plan
Continuous Optimization Checklist
-
[ ] Regularly evaluate recognition accuracy -
[ ] Collect edge cases and failure samples -
[ ] Monitor processing performance metrics -
[ ] Optimize batch processing parameters -
[ ] Update model version (when new version available)
One-Page Summary
PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 Core Points:
Model Features
-
0.9B parameter lightweight model -
94.5% accuracy on OmniDocBench v1.5 -
Supports real-world physical distortion processing -
Unified framework supports multiple document understanding tasks
Core Capabilities
-
Irregular shape localization -
Text spotting and recognition -
Table, formula, chart recognition -
Seal recognition -
Multilingual support -
Cross-page content processing
Quick Start
pip install paddlepaddle-gpu==3.2.1
pip install -U "paddleocr[doc-parser]"
paddleocr doc_parser -i image.png
Applicable Scenarios
-
Document digitization -
Automated contract review -
Batch invoice processing -
Academic literature extraction -
Archive management -
Form recognition
Performance Optimization
-
Use vLLM to accelerate batch processing -
Enable Flash Attention to reduce memory -
Set batch size appropriately -
Image preprocessing optimization
Key Reminders
-
Requires PaddlePaddle 3.2.1+ -
macOS users use Docker -
Production deployment recommends GPU acceleration -
Establish quality monitoring mechanism
Conclusion
PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 represents an important advance in document parsing technology. It’s not simply performance improvement but systematically solving key problems in document processing from real needs.
The 0.9B parameter scale proves vertical domains don’t need to blindly pursue large models. Targeted optimization, real-world scenario validation, complete capability systems—these are the keys to practical tools.
From my usage experience, this model’s greatest value lies in reliability. It can stably process various complex scenarios, reducing manual intervention needs. For enterprises needing batch document processing, this means real efficiency improvement and cost savings.
If you’re looking for a reliable document parsing solution, PaddleOCR-VL-1.5 is worth trying. It’s not omnipotent, but in the scenarios it covers, it has reached industry-leading levels. More importantly, it’s open-source—you can freely use, test, and even customize based on your needs.
Technological progress isn’t achieved overnight but gradually realized through continuously solving practical problems. PaddleOCR-VL-1.5’s release brings new possibilities to the document intelligence processing field. Looking forward to seeing more innovative applications based on this model.
Images in this article: PaddlePaddle Official GitHub Repository