
一、引言
在 AI 世界里,几乎每隔几个月都会有一个“新王者”的名字被喊出来。OpenAI、Anthropic、Google DeepMind、Mistral……这些名字已经占据了科技新闻头条。但这一次,主角换成了 Qwen3-Max ——一个由阿里团队推出的超大规模语言模型。
很多人第一时间会问:
-
“它和 GPT-5 比,强在哪儿?” -
“为什么说它是迄今为止最强的 Qwen 系列?” -
“普通开发者能用吗,还是只停留在实验室?”
别急,接下来我会用最直白的方式,带你看懂这个 1 万亿参数级别的巨兽。
二、Qwen3-Max 的总体概览
如果要用一句话总结 Qwen3-Max:
👉 它是 Qwen3 系列中规模最大、性能最强、应用面最广的模型。
-
参数规模:1 万亿参数(Trillion-Scale),这让它进入了超大模型俱乐部。 -
训练数据:36 万亿 tokens,几乎涵盖了人类公开知识的海洋。 -
架构:基于 Mixture of Experts (MoE),并在此基础上加入了“全球批次负载均衡损失”(global-batch load balancing loss)。
一句通俗的解释:Qwen3-Max 就像一支超级战队,每个“专家”专精不同技能,而系统能自动派遣合适的专家来完成任务。
为什么要强调“稳定性”?
过去很多大模型在训练中会遇到“损失曲线突然炸裂”的情况,就像股票闪崩,需要回滚或者重新分配数据。Qwen3-Max 解决了这个问题,训练曲线始终平滑,就像开车上高速一路绿灯。
三、核心技术与创新点
1. 稳定性优化
-
MoE 架构:让不同“专家”专注不同的输入,避免全员上阵导致效率低。 -
平滑的损失曲线:整个预训练过程没有出现过需要中断或回滚的情况。 -
无需临时补丁:以往常见的“换数据”“临时调参”完全没必要。
📌 打个比方,这就像你在跑马拉松,其他选手要不断停下来喝水、绑鞋带,而 Qwen3-Max 从头到尾几乎没掉速。
2. 训练效率提升
这里有几个关键成果:
-
PAI-FlashMoE 并行策略:把超大模型切分后,在硬件集群中像“多车道流水线”一样运行,让 GPU 不再浪费。 -
MFU 提升 30%:相比前一代 Qwen2.5-Max,利用率更高。 -
ChunkFlow 技术:突破性地支持 1M tokens 长上下文,训练吞吐量提升 3 倍。 -
容错机制:SanityCheck、EasyCheckpoint,避免硬件故障让训练重头来过。
如果你关心开发者友好性:这意味着未来你在调用 Qwen3-Max 时,可以扔给它一份“长达百万字的合同”或“整个大项目代码”,它依然能全局理解,而不是像传统模型那样“遗忘开头”。
四、Qwen3-Max-Instruct
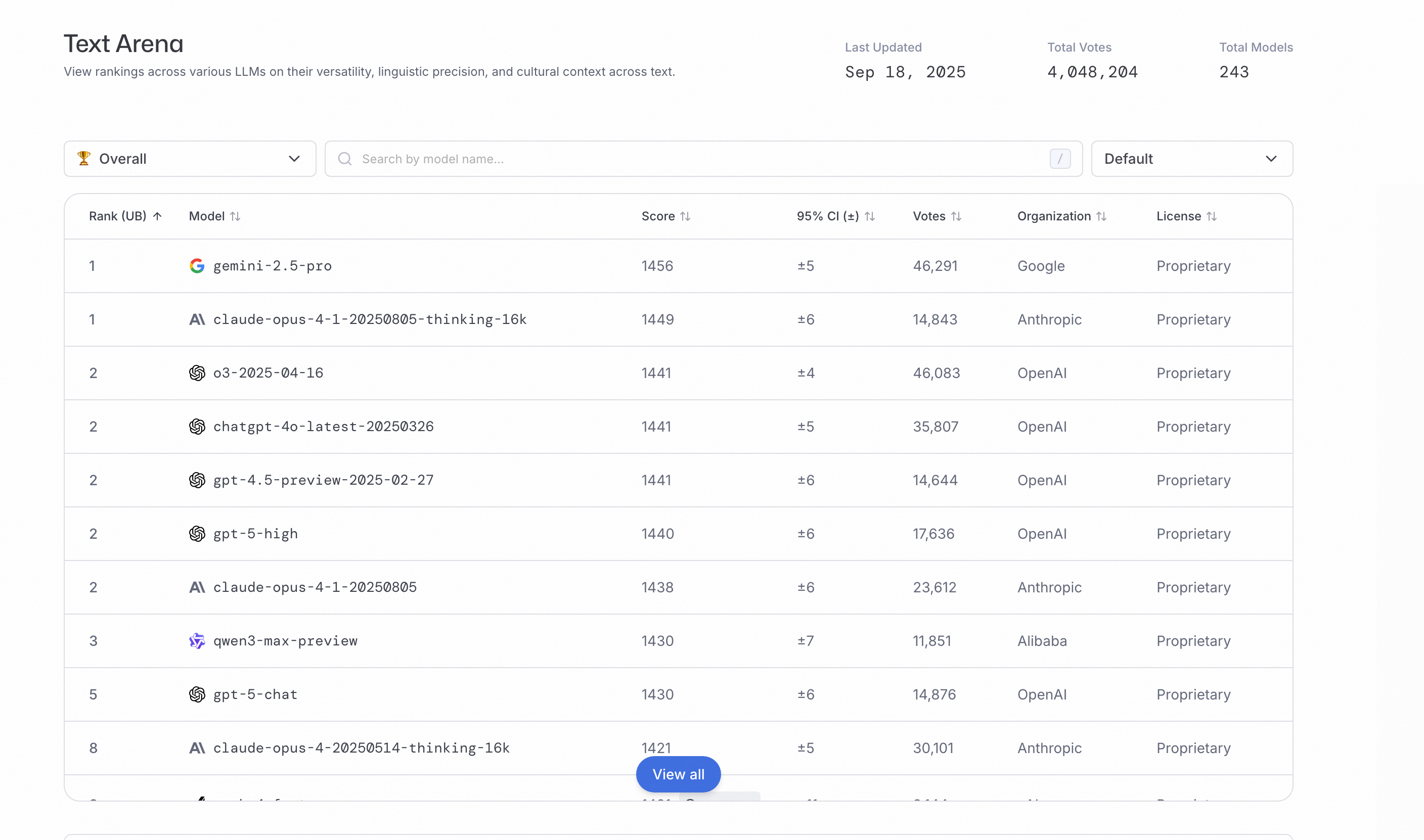
Qwen3-Max 的 指令微调版本,是普通用户和开发者最常用的版本。它的亮点主要体现在三个方面:
1. 榜单成绩
-
在 LMArena 榜单拿下全球前三(超过 GPT-5-Chat)。 -
在 Text Arena测试中排名领先。
2. 编程能力
-
在 SWE-Bench Verified(解决真实编程问题的基准)上得分 69.6。 -
这意味着它能自动修 Bug、补代码、写单元测试。
3. 智能体能力
-
在 Tau2-Bench(测试 AI 调用工具和组合操作能力的基准)上得分 74.8,超越了 Claude Opus 4 和 DeepSeek V3.1。
📌 换句话说,Qwen3-Max 不只是一个聊天机器人,而是一个能完成复杂“任务链”的 AI 助手。
五、Qwen3-Max-Thinking
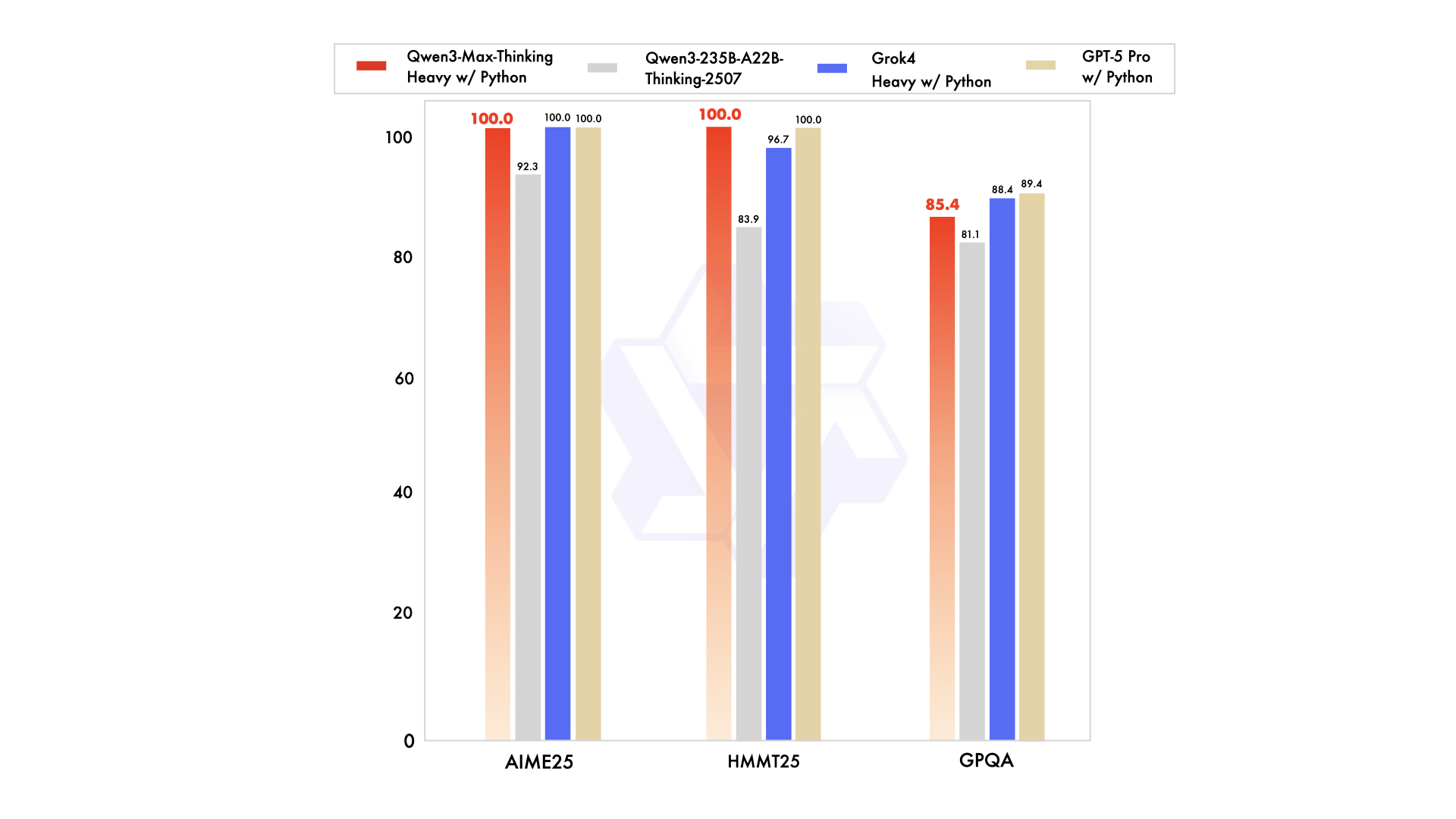
如果说 Instruct 是面向日常应用的“实干家”,那 Thinking 版就是推理专家。
-
集成 代码解释器,可以在思考过程中运行代码来验证答案。 -
支持 并行推理计算,让它在复杂任务上不只是“快”,而是“准确”。 -
在 数学竞赛基准(AIME 25 和 HMMT)上拿下 满分 100 分。
这意味着什么?
👉 未来它不仅能解答数学题,还能作为科学研究助手,帮科研人员做复杂证明或模拟。
六、开发与接入
对于开发者而言,最关心的问题是:我怎么用?
方式一:直接体验
你可以去 Qwen Chat 直接和 Qwen3-Max 对话。
方式二:API 调用
Qwen 的 API 与 OpenAI API 兼容,所以用法几乎一致。
步骤说明(HowTo)
-
注册阿里云账号 -
开通 Model Studio 服务 -
获取 API Key -
使用 Python SDK 调用
Python 示例
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(api_key="YOUR_API_KEY", base_url="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1")
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="qwen3-max",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "给我写一段快速排序代码"}
]
)
print(response.choices[0].message["content"])
是不是很熟悉?对,几乎和 OpenAI 一样。
七、学术与产业参考
Qwen3-Max 并不仅仅是“工程堆料”,它背后有扎实的学术研究支持:
-
Qwen3 Technical Report,系统介绍了架构与优化策略。 -
ACL25:关于负载均衡损失在 MoE 训练中的论文。 -
ICML25:ChunkFlow 的长上下文优化研究。
这些研究让 Qwen3-Max 不只是一个商用产品,也成为 AI 学界的参考案例。
八、常见问题(FAQ)
Q1:Qwen3-Max 和 GPT-5 谁更强?
目前在一些公开榜单上,Qwen3-Max-Instruct 已经超过 GPT-5-Chat,尤其是在代码和智能体能力上。
Q2:个人能用吗?
可以。直接去 Qwen Chat 免费试用,或者通过阿里云 API 接入。
Q3:它支持多语言吗?
是的,Qwen3 系列一直在多语言理解上表现优异,尤其在中文和英文的平衡度上远超大多数同类。
Q4:我能用它来做科研吗?
非常适合。尤其是 Qwen3-Max-Thinking,它在数学、逻辑推理上的表现堪称“学霸级别”。
Q5:和 Claude Opus 或 DeepSeek 比呢?
在 Tau2-Bench 智能体基准上,Qwen3-Max 已经领先于 Claude Opus 4 和 DeepSeek V3.1。
九、总结与展望
Qwen3-Max 是大模型竞赛中一位“后来居上”的选手,它的突破主要体现在:
-
稳定性:训练过程顺滑无比 -
效率:1M tokens 长上下文支持 -
能力:代码、智能体、推理全面领先 -
易用性:API 兼容 OpenAI,降低学习成本
未来可以预见,Qwen3-Max 将在三个方向产生巨大影响:
-
企业级 AI 应用:智能客服、流程自动化、代码生成。 -
科研与教育:数学推理、逻辑证明、知识问答。 -
开发者生态:更开放的 API,更低门槛的使用体验。
一句话总结:
👉 Qwen3-Max 不仅是“更大”,而是“更聪明、更稳定、更好用”。
十、对比一览:Qwen3-Max vs GPT-5 vs Claude Opus 4
在你选择大模型之前,最关心的一定是:它们到底差在哪?
下面这张表格可以让你一眼看出 Qwen3-Max、GPT-5 和 Claude Opus 4 的主要差异:
| 比较维度 | Qwen3-Max | GPT-5 (OpenAI) | Claude Opus 4 (Anthropic) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 参数规模 | 约 1T | 未披露 | 未披露 |
| 训练语料 | 36T tokens | 未公开 | 未公开 |
| 架构 | MoE + 负载均衡 + ChunkFlow | OpenAI 自研 Transformer 变体 | Anthropic Transformer 变体 |
| 长上下文 | 1M tokens 训练支持 | 长链改进(长度未统一公开) | Marathon Tasks(长度未披露) |
| 编码能力 | SWE-Bench:69.6 | 强调改进 | SWE-Bench:72.5 |
| Agent 能力 | Tau2-Bench:74.8 | 工具链集成强 | 长任务稳定性突出 |
| 可用性 | Qwen Chat + 阿里云 API | OpenAI 平台 + Microsoft Copilot | Anthropic 平台 |
| 适用场景 | 长文档、科研、智能体链路 | 多模态、企业生态 | 长时间 Agent、工程任务 |
十一、工程师快速上手对比建议(HowTo)
很多开发者都会问:
“我该怎么判断哪个模型最适合我的业务?”
答案是:不要光看参数和广告,自己跑一遍 PoC 就知道。
步骤一:明确你的业务场景
-
如果你是做代码自动化 → 可以用常见的修 Bug / 单元测试生成任务。 -
如果你是做客服/文档处理 → 可以扔一份长达几十页的合同,测试是否能保持上下文一致。 -
如果你是科研人员 → 尝试数理逻辑题或复杂推理问题。
步骤二:准备测试脚本
你可以用 Python 同时调用不同模型的 API,收集结果。
from openai import OpenAI
# 替换 base_url 和 model 名称即可调用 Qwen3-Max 或 OpenAI GPT-5
def run_test(api_key, base_url, model, prompt):
client = OpenAI(api_key=api_key, base_url=base_url)
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
)
return response.choices[0].message["content"]
# 示例:运行对比测试
prompts = [
"请帮我写一个快速排序的 Python 函数,并加上注释。",
"阅读这份 20 页的合同,总结关键风险条款。",
"解答:已知 2x+3=11,求 x。"
]
for p in prompts:
print("Qwen3-Max:", run_test("YOUR_QWEN_KEY", "https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1", "qwen3-max", p))
print("GPT-5:", run_test("YOUR_OPENAI_KEY", "https://api.openai.com/v1", "gpt-5-chat", p))
步骤三:评估指标(重点关注四个维度)
| 指标 | 说明 | 如何测量 |
|---|---|---|
| 正确率(Accuracy) | 答案是否符合预期 | 对数学题/代码可写自动化判定脚本 |
| pass@k | 在生成多份代码时,至少有 1 份正确的概率 | 常用于代码基准(如 HumanEval) |
| 延迟(Latency) | 响应速度 | 用 time 模块记录 API 响应时间 |
| 成本(Cost) | Token 消耗与价格 | 查看 API 返回的 usage 字段,结合厂商定价计算 |
步骤四:小规模验证(PoC)
-
选 10~20 个常见任务,跑通三个模型。 -
记录每个任务的 正确率、延迟、成本。 -
根据结果选择最适合自己业务的模型。
十一、总结与实战建议
-
别盲信广告:参数再大、榜单再高,都不如你自己测过来得真实。
-
选场景匹配的模型:
-
需要超长上下文 → 试试 Qwen3-Max -
需要多模态和生态 → 考虑 GPT-5 -
需要长时间稳定的智能体 → Claude Opus 4 更合适
-
-
持续更新测试:厂商会不断更新模型,你的评估脚本要保持可复用。
一句话建议:
👉 工程师的最佳选择,是用自己的任务做 Benchmark,而不是只看厂商 PPT。
一个开箱即用的 Python 工具脚本,功能齐全、结构清晰,可以直接用于对比 Qwen3-Max / GPT-5 / Claude Opus 4 等 OpenAI-compatible 模型的性能(包括响应、延迟、自动评分、代码执行验证、结果 CSV 导出)。脚本里包含:
-
并发调用不同模型的 API(可配置 base_url,支持 Qwen 的兼容模式) -
对 数学题/短问答/代码生成/长文摘要 等常见任务的自动化评估逻辑 -
对代码任务做 自动运行 + 单元测试(pass/fail) 的判定(带超时与安全提醒) -
记录延迟、模型返回字段(若厂商返回 usage 则记录 tokens/cost info) -
将结果按行写出 CSV,便于后续统计或画图分析
⚠️ 重要安全提醒:脚本中会把模型生成的代码写入临时文件并执行以做单元测试。切勿在不受信任的环境中运行这些自动生成的脚本。强烈建议在隔离环境中运行(如 Docker 容器、受限制的 VM 或沙箱),并为
subprocess执行设置严格资源/时间限制。
下面是完整脚本(保存为 multi_model_benchmark.py),随后我会给出使用说明、配置项、示例 prompt 集,以及一个简单的 JSON-LD HowTo(可直接嵌入博客页面以改善搜索意图匹配)。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# multi_model_benchmark.py
# Multi-model benchmarking framework for OpenAI-compatible APIs (Qwen3-Max, GPT-5, Claude Opus 4...)
# Features:
# - configurable models (api_key, base_url, model_name)
# - prompt sets for math / code / summarization
# - automatic scoring for math and code (unit test run)
# - latency, usage capture (if returned), CSV export
#
# SECURITY: This script will execute generated code in a subprocess for code-checking.
# Run only in sandboxed environment (docker container, restricted VM).
#
# Dependencies: requests, pandas (optional), python >= 3.8
# Install: pip install requests pandas
#
# Usage: set environment variables for API keys (or edit the config block below).
# python multi_model_benchmark.py
import os
import time
import json
import csv
import uuid
import tempfile
import subprocess
from datetime import datetime
from typing import Dict, Any, List, Optional
import requests
# ------------- Configuration -------------
# Define models you want to test. For each:
# - name: display name
# - api_key_env: environment variable name that stores the API key
# - base_url: endpoint base url for OpenAI-compatible API (e.g. Qwen compatible endpoint or OpenAI)
# - model: model id to request
MODELS = [
{
"name": "Qwen3-Max",
"api_key_env": "QWEN_API_KEY",
"base_url": "https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1", # example from Qwen docs
"model": "qwen3-max"
},
{
"name": "GPT-5",
"api_key_env": "OPENAI_API_KEY",
"base_url": "https://api.openai.com/v1",
"model": "gpt-5-chat"
},
{
"name": "Claude-Opus-4",
"api_key_env": "CLAUDE_API_KEY",
"base_url": "https://api.anthropic.com/v1", # placeholder: anthopic has different interface
"model": "claude-opus-4" # may need custom adapter; here shown for completeness
}
]
# CSV output file
OUTPUT_CSV = "benchmark_results.csv"
# Global request timeout (seconds)
REQUEST_TIMEOUT = 60
# Code execution timeout for running generated code (seconds)
CODE_EXEC_TIMEOUT = 6
# Max tokens per request (optional)
MAX_TOKENS = 2048
# ------------- Prompt Suite -------------
# Each prompt has:
# - id
# - type: 'math'|'code'|'summary'|'qa'
# - prompt: the actual prompt to send to the model
# - reference: correct answer or tests (for automatic scoring). For code tests, provide 'unit_tests' as Python code to run.
PROMPTS = [
{
"id": "math_01",
"type": "math",
"prompt": "解答:已知 2*x + 3 = 11,求 x 的值并说明步骤。",
"reference": "4" # expected numeric answer as string
},
{
"id": "code_qs_01",
"type": "code",
"prompt": "请用 Python 写一个函数 `quick_sort(arr)` 返回排序后的数组,带注释和举例。",
"reference": {
# unit_tests: python code that imports function from file and runs asserts
"unit_tests": """
import json,sys
from quick_impl import quick_sort
assert quick_sort([3,1,2]) == [1,2,3]
assert quick_sort([]) == []
assert quick_sort([5,4,3,2,1]) == [1,2,3,4,5]
print("PASS")
"""
}
},
{
"id": "summary_01",
"type": "summary",
"prompt": ("下面是一个长文本(模拟合同 / 报告):\n" +
"Alice 与 Bob 签订合同,约定 Bob 在 2025 年交付项目,若延期每天扣款 1000 美元,"
"并约定保密条款、不可抗力条款,以及争议由伦敦仲裁解决。请总结关键风险点(不超过120字)。"),
# For summary, reference is optional; we will accept manual/heuristic judgement
"reference": None
}
]
# ------------- Helpers -------------
def get_api_key(model_cfg):
return os.getenv(model_cfg["api_key_env"], None)
def build_chat_payload_openai_style(messages: List[Dict[str, str]], model: str, max_tokens: int = MAX_TOKENS):
return {
"model": model,
"messages": messages,
"max_tokens": max_tokens,
"temperature": 0.0
}
def call_model(model_cfg: Dict[str, Any], messages: List[Dict[str, str]]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
Use HTTP POST to the base_url + '/chat/completions' if compatible.
This is a simple, generic caller — may need adaptation for Anthropic or non-compatible endpoints.
"""
api_key = get_api_key(model_cfg)
if not api_key:
return {"error": f"No API key found in env {model_cfg['api_key_env']}"}
# Try OpenAI-compatible chat completions endpoint
url = model_cfg["base_url"].rstrip("/") + "/chat/completions"
payload = build_chat_payload_openai_style(messages=messages, model=model_cfg["model"])
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {api_key}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
start = time.time()
try:
resp = requests.post(url, json=payload, headers=headers, timeout=REQUEST_TIMEOUT)
latency = time.time() - start
resp.raise_for_status()
data = resp.json()
# Try to extract usage tokens if present
usage = data.get("usage", {})
# Extract first assistant message text
content = None
try:
content = data["choices"][0]["message"]["content"]
except Exception:
# fallback: sometimes choices[0].text exists
content = data["choices"][0].get("text")
return {"ok": True, "data": data, "latency": latency, "usage": usage, "content": content}
except requests.RequestException as e:
latency = time.time() - start
return {"ok": False, "error": str(e), "latency": latency}
# ------------- Scoring -------------
def score_math(response_text: str, reference: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
Very simple numeric extraction and exact match.
"""
# extract first integer/float-like token from response
import re
m = re.search(r"(-?\d+(\.\d+)?)", response_text)
if m:
ans = m.group(1)
match = str(ans).strip() == str(reference).strip()
return {"score": 1.0 if match else 0.0, "answer_extracted": ans, "match": match}
else:
return {"score": 0.0, "answer_extracted": None, "match": False}
def score_code_by_running(code_text: str, unit_tests: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
Write code_text into a temp file as quick_impl.py, then write unit_tests into a runner file and execute.
Returns pass/fail and exec logs. Timeout enforced.
SECURITY WARNING: executing arbitrary code. Use sandbox.
"""
tmpdir = tempfile.mkdtemp(prefix="bench_")
impl_path = os.path.join(tmpdir, "quick_impl.py")
runner_path = os.path.join(tmpdir, "run_tests.py")
# try to extract only code block if markdown fences present
if "```" in code_text:
# naive extraction: take first code fence content
parts = code_text.split("```")
# if first fence has language, parts[1] is code; else fallback
if len(parts) >= 2:
code_text = parts[1]
with open(impl_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(code_text)
with open(runner_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(unit_tests)
# run runner using subprocess with timeout
try:
proc = subprocess.run(
["python", runner_path],
cwd=tmpdir,
capture_output=True,
text=True,
timeout=CODE_EXEC_TIMEOUT
)
success = proc.returncode == 0
stdout = proc.stdout
stderr = proc.stderr
return {"success": success, "stdout": stdout, "stderr": stderr, "returncode": proc.returncode}
except subprocess.TimeoutExpired as e:
return {"success": False, "stdout": e.stdout or "", "stderr": "TimeoutExpired", "returncode": -1}
except Exception as e:
return {"success": False, "stdout": "", "stderr": f"ExecError: {e}", "returncode": -2}
# ------------- Runner -------------
def run_benchmark(models: List[Dict[str, Any]], prompts: List[Dict[str, Any]], output_csv: str = OUTPUT_CSV):
fieldnames = [
"timestamp", "run_id", "model_name", "prompt_id", "prompt_type",
"latency_s", "ok", "error", "usage", "score", "pass_bool",
"response_snippet", "full_response", "exec_stdout", "exec_stderr"
]
run_id = str(uuid.uuid4())[:8]
with open(output_csv, "a", newline="", encoding="utf-8") as csvfile:
writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
# write header if empty
if csvfile.tell() == 0:
writer.writeheader()
for m in models:
for p in prompts:
timestamp = datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
# prepare messages for chat
# system prompt to force consistent behavior
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant. Please answer concisely."},
{"role": "user", "content": p["prompt"]}
]
print(f"[{timestamp}] Running {m['name']} on prompt {p['id']} ({p['type']}) ...")
res = call_model(m, messages)
row = {
"timestamp": timestamp,
"run_id": run_id,
"model_name": m["name"],
"prompt_id": p["id"],
"prompt_type": p["type"],
"latency_s": round(res.get("latency", 0), 3),
"ok": res.get("ok", False),
"error": res.get("error", "") if not res.get("ok", False) else ""
}
if res.get("ok"):
usage = res.get("usage", {})
row["usage"] = json.dumps(usage, ensure_ascii=False)
content = res.get("content", "")
row["response_snippet"] = (content[:300] + "...") if content else ""
row["full_response"] = content
# scoring
score = None
pass_bool = None
exec_stdout = ""
exec_stderr = ""
if p["type"] == "math":
sc = score_math(content or "", p.get("reference"))
score = sc["score"]
pass_bool = sc["match"]
elif p["type"] == "code":
unit_tests = p["reference"]["unit_tests"]
# content may include explanation + code block
sc = score_code_by_running(content or "", unit_tests)
pass_bool = sc["success"]
score = 1.0 if pass_bool else 0.0
exec_stdout = sc.get("stdout", "")
exec_stderr = sc.get("stderr", "")
elif p["type"] == "summary":
# placeholder: no automatic scoring; leave to manual review
score = None
pass_bool = None
else:
score = None
pass_bool = None
row.update({
"score": score,
"pass_bool": pass_bool,
"exec_stdout": exec_stdout,
"exec_stderr": exec_stderr
})
else:
row.update({"usage": "", "response_snippet": "", "full_response": "", "score": None, "pass_bool": False})
writer.writerow(row)
# flush to disk
csvfile.flush()
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("Starting multi-model benchmark. Models configured:")
for mm in MODELS:
print("-", mm["name"])
print("Prompts to run:", len(PROMPTS))
run_benchmark(MODELS, PROMPTS, OUTPUT_CSV)
print("Done. Results written to", OUTPUT_CSV)
使用与部署说明(一步步)
1) 环境准备
-
Python 3.8+ 推荐 -
安装依赖:
pip install requests pandas
2) 准备 API Key(环境变量)
把各模型 API Key 设置为环境变量(或直接改脚本里的 MODELS 配置,不建议把密钥写死在脚本):
export QWEN_API_KEY="你的_qwen_api_key"
export OPENAI_API_KEY="你的_openai_api_key"
export CLAUDE_API_KEY="你的_claude_api_key"
Qwen 的例子使用了兼容 OpenAI 的 endpoint
https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1。如果你使用的是阿里云控制台提供的终端或其它路径,请把base_url改成正确的地址。
3) 运行脚本(强烈建议在容器中运行)
建议在 Docker 或受限 VM 中运行:
python multi_model_benchmark.py
脚本会将每次模型对每个 prompt 的结果写入 benchmark_results.csv。
4) 读取结果
CSV 包含字段(部分):
-
timestamp、model_name、prompt_id、latency_s、usage(如果服务返回) -
score(自动判分)与pass_bool(code pass/fail) -
full_response(模型原始返回)与exec_stdout/exec_stderr(代码执行记录)
可用 pandas 做可视化或导入 Excel 分析:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv("benchmark_results.csv")
print(df.groupby("model_name")["latency_s"].mean())
如何扩展(建议)
-
扩展 Prompt Suite:把更多业务问题、edge case 加入 PROMPTS(例如多轮对话、API 调用链、长文档 >50k tokens 测试等)。 -
更严格的代码沙箱:使用 Docker、gVisor、或 Linux cgroups 来限制 CPU、内存和文件系统访问。 -
更多自动评估指标:集成 rouge,bleu(摘要/翻译评估)、pytest(复杂测试)或专用评估脚本。 -
并发请求:如果要测吞吐,加入 concurrent.futures并发发送请求来模拟并发负载。 -
成本估算:从 usage字段提取prompt_tokens/completion_tokens,结合厂商的定价做成本估算(该脚本已保留 usage 字段以便后续计算)。
示例输出(CSV 列示例)
timestamp,run_id,model_name,prompt_id,prompt_type,latency_s,ok,error,usage,score,pass_bool,response_snippet,full_response,exec_stdout,exec_stderr
2025-09-24T10:00:00Z,abcd1234,Qwen3-Max,code_qs_01,code,1.234,True,,{"prompt_tokens":100,"completion_tokens":200},1.0,True,"def quick_sort...","<full text>", "PASS", ""
FAQ(常见问题)
Q:脚本能直接评测 Anthropic / Claude 吗?
A:理论上可以,但 Anthropic 的 API(及其鉴权/请求格式)与 OpenAI 兼容层可能不同。上面脚本针对 OpenAI-style Chat Completions 接口。若用 Anthropic,请根据其官方 API 调整 call_model 函数或写一个适配器。
Q:如何评估长上下文(如 1M tokens)能力?
A:实际测试需要分片上传长文本或通过流式/分段上下文测试。由于大多数公开 API 在请求大小上有限制,你需要把 PROMPTS 设计成分段交互并考察模型是否能维持跨段一致性(或使用厂商专门的长上下文接口/批量上传方式)。
Q:如何把成本计算自动化?
A:当响应中有 usage 字段(prompt_tokens, completion_tokens)时,用这些数乘以厂商当前单价即可得到估算成本。建议把单价放在 config 并让脚本输出 cost_estimate 字段。
JSON-LD HowTo(嵌入博客页面,帮助搜索引擎理解“如何进行模型对比”)
你可以把下面 JSON-LD 放入博客 <head> 或文章底部,标注为 HowTo:
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "HowTo",
"name": "如何做多模型对比测试(Qwen3-Max / GPT-5 / Claude Opus 4)",
"description": "一步步搭建简单的多模型基准测试框架,包含自动评分、代码执行验证与 CSV 导出",
"step": [
{"@type":"HowToStep","name":"准备环境","text":"Python 3.8+,安装 requests、pandas,准备 API keys。"},
{"@type":"HowToStep","name":"下载脚本","text":"保存 multi_model_benchmark.py 并配置 MODELS。"},
{"@type":"HowToStep","name":"运行脚本","text":"在隔离环境中运行 python multi_model_benchmark.py,结果写入 CSV。"},
{"@type":"HowToStep","name":"分析结果","text":"用 pandas 或 Excel 加载 CSV,比较延迟、正确率与成本。"}
]
}
</script>

