Davia: The Simplest Way to Build Web Apps from Python Code
Transform Python scripts into professional web applications in minutes—zero frontend skills required
The Python Developer’s Dilemma
How often do you face this situation? 🤔
Your powerful data processing script or AI model works perfectly in the terminal but becomes useless when colleagues need a visual interface. You spend three weeks building an internal tool—two of those wrestling with React components. Clients demand real-time analytics, but WebSocket implementation eats your development time…
Davia was born to solve these exact pain points! This revolutionary framework lets you create production-ready web apps using pure Python, perfect for:
-
✦ ✅ Visualizing AI agents -
✦ ✅ Building data dashboards -
✦ ✅ Creating internal tools -
✦ ✅ Deploying algorithm services
Why Developers Love Davia
Three Game-Changing Advantages
-
Minimalist Development
Imagine: A decorator transforms ordinary functions into web endpoints -
Automatically Generated UI
Powered by industry-standard shadcn/ui components:-
✦ Light/dark mode auto-switching -
✦ Mobile-responsive design -
✦ Accessibility compliant -
✦ Real-time data streaming
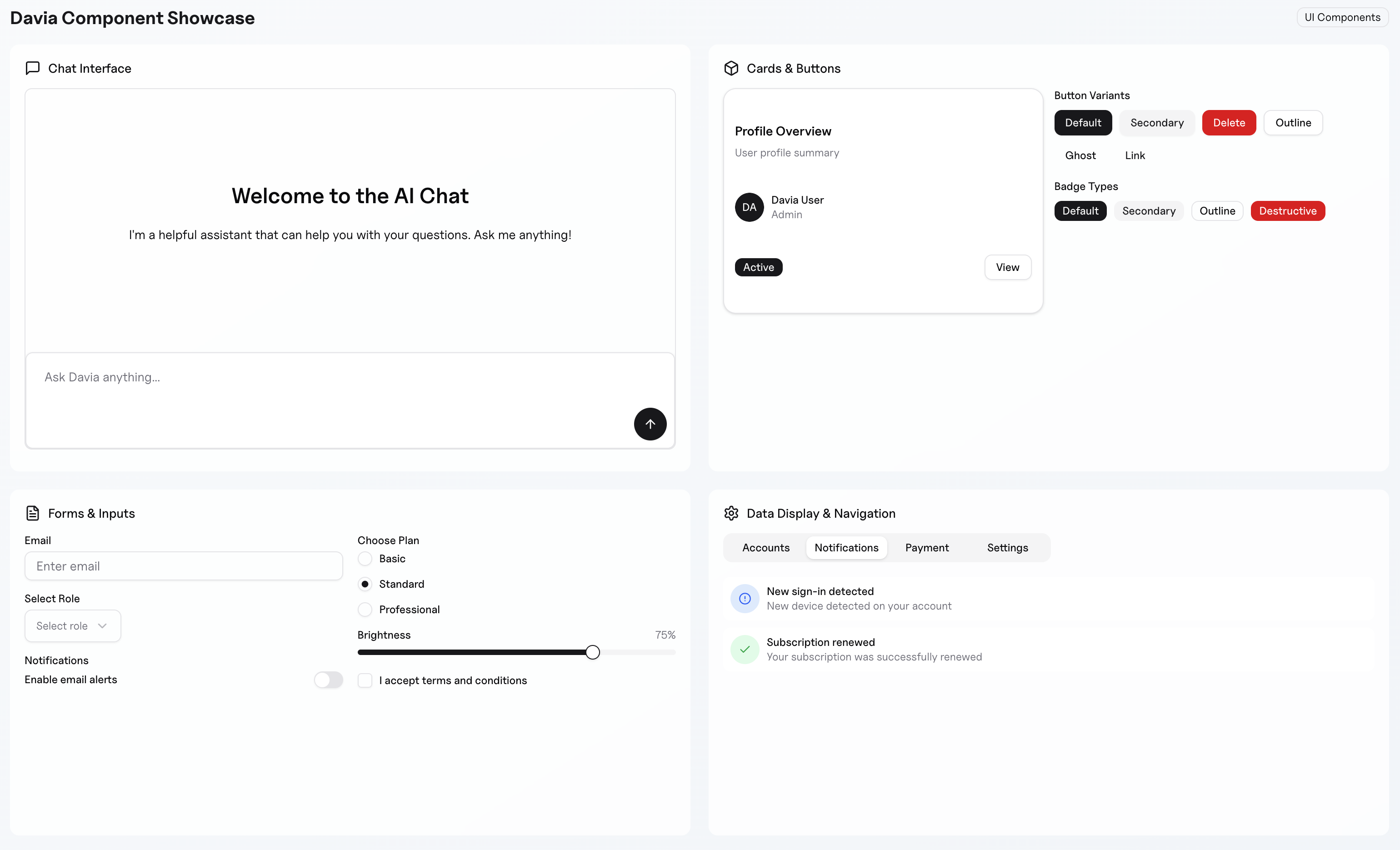
Sales Analysis Interface by Davia -
-
Out-of-the-Box Real-Time Communication
No more WebSocket configuration headaches:
Architectural Blueprint
From Zero to Production in 5 Minutes
Installation Made Simple
Build Your First App
-
Create demo.py:
-
Launch the server:
-
Visit the dashboard URL in your browser (typically https://davia.ai/dashboard)
Professional Development Practices
-
Type Declarations = Superpower
Use Pydantic models for robust data validation:
-
Docs Become UI
Well-crafted docstrings automatically generate interface guides:
Advanced Mastery
Seamless FastAPI Integration
Built on FastAPI for enterprise-grade performance:
AI Agent Visualization
LangGraph developers rejoice:
Under the Hood
UI Auto-Generation Logic
Real-Time Communication Engine
Top 8 Developer Questions
Q1: Production-ready?
✅ Industrial-grade FastAPI foundation
✅ Kubernetes deployment support
✅ Built-in error circuit breakers
Q2: Customizable UI?
✅ Modify themes via CSS variables
✅ Inject custom React components
✅ Layout API coming soon
Q3: Database connections?
Q4: User authentication?
✅ Integrated FastAPI security
✅ OAuth2/JWT support
✅ Permission decorators in development
Q5: Large file handling?
💡 Chunked transfer technology
💡 <10MB memory footprint
💡 Resume upload support
Q6: Export standalone frontend?
🚧 Requires backend in current version
✨ Future React code export planned
Q7: Mobile experience?
📱 Responsive layouts
📱 Touch-optimized controls
📱 PWA support roadmap
Q8: Performance monitoring?
🔍 Built-in Prometheus metrics
🔍 Datadog integration
🔍 Profiling mode
Real-World Implementations
Case 1: Smart Sales Dashboard
Case 2: AI Customer Service Trainer
Learning Resources
Skill Development Path
-
Foundations → 5-Minute Quickstart -
Advanced Techniques → Task Definition Guide -
AI Agents → LangGraph Integration
Troubleshooting Support
-
✦ Official Docs: docs.davia.ai -
✦ Issue Tracking: GitHub Issues -
✦ Community: Discord Channel (Coming soon)
Technical Ecosystem
Version Compatibility Matrix
Core Dependencies
Start Your Davia Journey
As the Davia team puts it: “From Python to App in seconds.”
Now focus on creating value—not configuring environments.
Further Exploration

