CoAct-1: Revolutionizing Computer Automation with Hybrid AI Agents
Introduction: The Evolution of Digital Task Automation
Imagine you’re managing a complex workflow that requires simultaneous use of multiple software tools. You need to extract data from an Excel spreadsheet, process images in Photoshop, and send the results via email—all while maintaining precision across different interfaces. Traditional AI systems that rely solely on graphical user interface (GUI) interactions would navigate this scenario through a series of mouse clicks and keyboard inputs, much like a human user would. However, these systems face significant challenges when dealing with:
-
Visual ambiguity: Similar-looking buttons or menu items -
Error accumulation: Small mistakes compounding through multi-step processes -
Cross-application complexity: Different software environments requiring unique interaction patterns
This is where CoAct-1 emerges as a groundbreaking solution. Developed by researchers from Salesforce and the University of Southern California, this hybrid AI system combines traditional GUI operations with programmatic execution capabilities, achieving a 60.76% success rate on the challenging OSWorld benchmark—significantly outperforming previous state-of-the-art systems.
The Limitations of Pure GUI-Based AI Systems
Visual Recognition Challenges
Modern GUI agents like OpenAI’s CUA 4o operate through vision-language models that analyze screen pixels to identify UI elements. While effective for simple tasks, these systems struggle with:
-
Icon ambiguity: Distinguishing between visually similar elements (e.g., document vs. PDF icons) -
Interface variations: Adapting to different software versions or custom UI layouts -
Long sequential errors: Each step introduces potential failure points
In OSWorld benchmark tests, traditional GUI-only approaches achieved only 8.91% success rates on multi-application tasks requiring more than 15 steps.
Real-World Complexity Example
Consider a task like “organize project files”:
1. Navigate to D:/projects directory
2. Filter .py files modified in 2024
3. Sort by code line count
4. Copy top 10 files to desktop
5. Compress into report.zip
6. Email via Outlook to team@company.com
A GUI-based AI would need to precisely identify each folder icon, file attribute location, and menu option through visual analysis alone—prone to errors at each step.
CoAct-1’s Innovative Hybrid Architecture
Three Specialized Agents Working in Concert
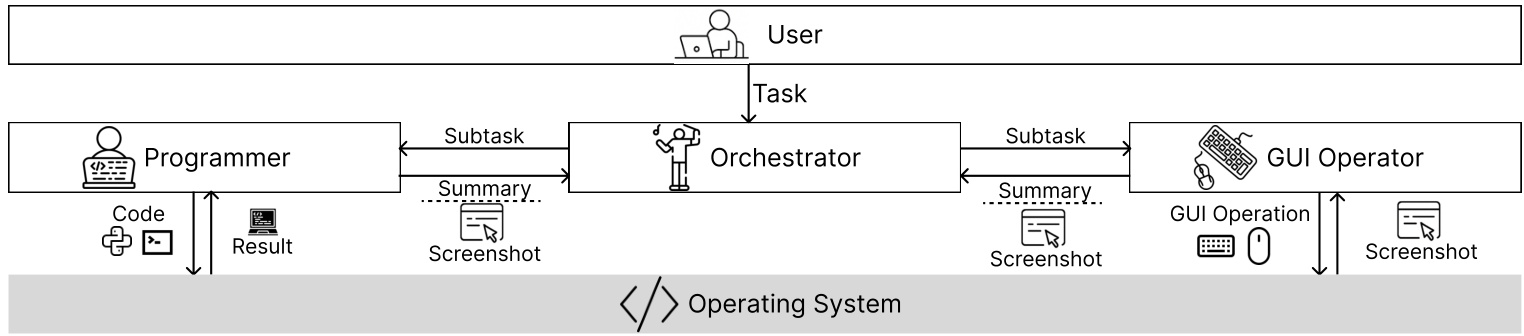
The system employs three distinct agents:
| Component | Function | Technology Basis |
|---|---|---|
| Orchestrator | Task decomposition & decision-making | Language model |
| Programmer | Python/Bash script generation | Code generation model |
| GUI Operator | Traditional interface interaction | Vision-language action model |
Dynamic Task Allocation Process
-
User request: “Convert all images in Downloads to PNG format” -
Orchestrator analysis: Identifies file operations → delegates to Programmer -
Programmer generates: import os from PIL import Image for root, dirs, files in os.walk("~/Downloads"): for file in files: if file.lower().endswith(('.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg')): img = Image.open(os.path.join(root, file)) img.save(os.path.splitext(file)[0] + '.png') -
Execution feedback loop ensures task completion verification
Efficiency Breakthrough: Data-Driven Advantages
Performance Metrics (100-step budget)
| Metric | Traditional GUI | CoAct-1 | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avg. steps | 15.22 | 10.15 | 33% reduction |
| Multi-app success | 38.34% | 47.88% | 25% increase |
| OS-level tasks | 62.50% | 75.00% | 20% increase |
Domain-Specific Performance
CoAct-1 shows remarkable improvements in:
-
File management: 70% fewer clicks -
Data processing: Complex calculations in single steps -
Email automation: Automatic generation of properly formatted content
Technical Deep Dive: How CoAct-1 Works
1. Orchestrator: The Task Manager
The central controller:
-
Monitors system state (open windows/file paths) -
Uses decision matrix: if task involves file operations or data processing: assign to Programmer elif requires interface clicks or unknown software: assign to GUI Operator
2. Programmer: The Code Generator
Key capabilities:
-
Supports Python/Bash scripting -
Multi-round code refinement -
Receives environment context from Orchestrator
3. GUI Operator: The Visual Specialist
Based on OpenAI CUA 4o:
-
Excels at: -
Graphic design software (GIMP operations) -
Complex browser interactions -
Exploratory navigation of unfamiliar interfaces
-
Memory Management System
Independent memory systems:
-
Orchestrator: Maintains complete task progress -
Programmer: Only retains current code conversation -
GUI Operator: Stores last 25 interface states
Real-World Applications
Developer Productivity Enhancement
Example: Debugging environment configuration
Traditional approach:
1. Open VSCode
2. Install Python extension
3. Configure debug settings
4. Set breakpoints
5. Start debugging
6. Discover terminal not activated
7. Switch tabs to start terminal
8. Repeat...
CoAct-1 solution:
Programmer generates launch.json configuration:
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [{
"name": "Python: Current File",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${file}",
"console": "integratedTerminal"
}]
}
Efficiency gain: 8 steps → 1 line of code
Office Automation
Case study: Quarterly report generation
# Programmer-generated script
import pandas as pd
from docx import Document
# Data processing
sales = pd.read_excel('q4_sales.xlsx')
summary = sales.groupby('region').sum()
# Report generation
doc = Document()
doc.add_heading('2024 Q4 Sales Report')
for region, data in summary.iterrows():
doc.add_paragraph(f"{region}: ${data['revenue']:,.2f}")
doc.save('report.docx')
Efficiency gain: Saves 15 Excel formula inputs + 10 Word formatting clicks
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Does CoAct-1 require internet connectivity?
Current version requires RESTful interface to remote VM for code execution, theoretically supports local deployment.
Q2: Is Chinese language support available?
Paper doesn’t specify language limitations, but architecture allows different language models.
Q3: How are programming errors handled?
Orchestrator receives execution feedback:
-
GUI Operator checks error messages -
Reassigns Programmer for code correction -
Up to 3 iteration cycles
Q4: What are hardware requirements?
-
Minimum: 4-core CPU + 16GB RAM -
Recommended: GPU-accelerated code execution (CUDA environment)
Future Development Directions
Current limitations:
-
Language support: Only Python/Bash currently -
Complex UI recognition: Needs improvement for dynamic web elements -
Security mechanisms: Lacks permission management
CoAct-2 development focuses on:
-
Additional language support (JavaScript/Shell) -
Enhanced UI element semantic understanding -
Secure sandbox implementation
Conclusion
CoAct-1’s innovative “programming + interface” hybrid architecture opens new possibilities for computer automation. It demonstrates significant advantages in scenarios requiring precise operations and data processing, particularly suited for:
-
Development toolchain automation -
Enterprise workflow optimization -
Complex data processing tasks
As AI code generation capabilities advance, such hybrid architectures may become standard for intelligent agent systems. Just as smartphones combine touchscreens and voice assistants, future AI assistants should flexibly choose the most appropriate interaction method.
Paper URL: https://linxins.net/coact/
OSWorld Benchmark: https://os-world.github.io/

